Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle cell disease is a group of inherited red blood cell disorders. People with sickle
cell have a problem with hemoglobin professionalagmarketing, which is the protein in red blood cells that
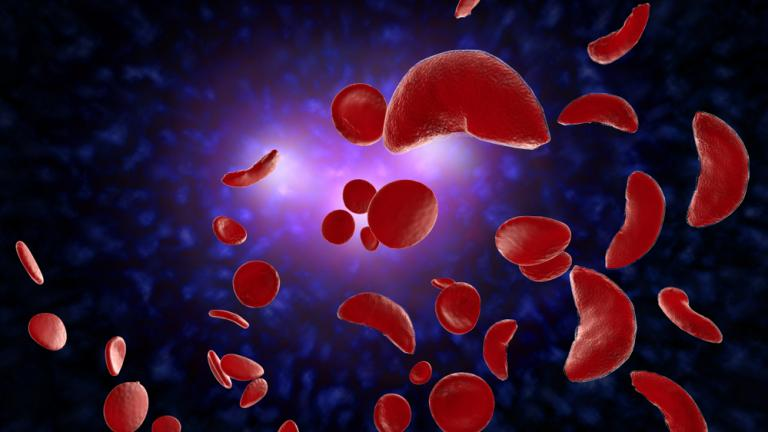
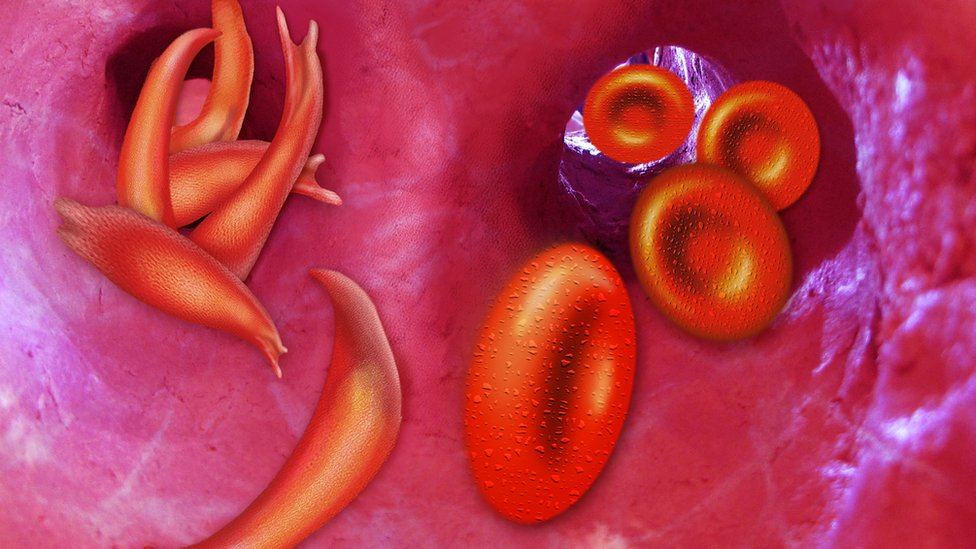
carries oxygen to all parts of the body. Hemoglobin molecules in people with sickle
cell disease stick together to form long, rod-like structures that change the shape of
red blood cells from their normal disc (shaped) to a sickle, or crescent, shape. These
shaped cells can get stuck in small blood vessels and block the flow of blood, which
can cause pain and damage tissues and organs.
A blood test called a hemoglobin electrophoresis can identify sickle cell disease in
newborns or infants. This is one of the tests performed during routine newborn
screening for serious, life-threatening diseases.
People with sickle cell have a higher risk for stroke, infections and other problems.
This is because their red blood cells don’t last as long and are destroyed more
quickly than normal, resulting in anemia. Anemia can make you feel tired and short
of breath, and it may make it harder to fight off infections.
The sickled red blood cells also clog small blood vessels, especially in the lungs. This
causes a problem called acute chest syndrome (ACS), which is a very serious
condition that makes it hard to breathe and can lead to pneumonia or lung failure.
People with sickle cell often have painful episodes (sickle cell crises), which can
occur anywhere in the body and last from hours to days. The episodes can be
triggered by colds, infections, fever, dehydration or stress.
Sickle cell disease can damage the spleen and kidneys. People with sickle cell have
a high risk of developing gallstones and can have trouble passing urine due to the
damage to the ureters, the tubes that carry urine from the kidneys. People with
sickle cell often have an enlarged liver, which can cause swelling in the abdomen
(hepatomegalya).
A drug called hydroxyurea can help reduce pain episodes and reduce the need for
blood transfusions in people with sickle cell disease. This medicine, taken as a pill
daily, increases the production of fetal hemoglobin, which helps prevent the sickling
of red blood cells. A stem cell transplant might cure some children and teenagers
with sickle cell disease by replacing the sick cells with healthy ones. This procedure
is done in a hospital with a team of health care professionals who specialize in sickle
cell disease.
